IT Manager
Job Description
Computer and information systems managers direct the work of systems analysts, computer programmers, support specialists, and other computer-related workers. These managers plan and coordinate installation and upgrading of hardware and software, programming and systems design, development of computer networks, and implementation of Internet and intranet sites. They’re increasingly involved with the upkeep, maintenance, and security of networks. They analyze the computer and information needs of their organizations and determine immediate and long-range personnel and equipment requirements. They assign and review the work of their subordinates and stay abreast of the latest technology to ensure the organization doesn’t lag behind competitors.
Education Requirements
Many managers possess advanced technical knowledge gained from working in a computer occupation.Job opportunities will be best for applicants with computer-related work experience; a master’s degree in business administration (MBA) with technology as a core component, or a management information systems degree; and strong communication and administrative skills.
Job Outlook
Employment of computer and information systems managers is expected to grow by 16% from 2006 to 2016.
Interface Architect
Job Description
Any company that’s building a new application, Web site, or video game faces some important decisions about how users will navigate and interact with their product. That’s where User Interface (or UI) Architects come in. UI Architects think about the way users will flow through an application, create flowcharts and wireframes mapping out interactions, and work with designers to create the look and feel of an interface. often, they work with focus groups and researchers to gather feedback from users and tweak interfaces for more efficiency.
Education Requirements
UI Architects come from a variety of fields. Most hold at least a BA or BS in design, human computer interaction, psychology, or library science, and an advanced degree in one of those fields is preferable.
Job Outlook
Job opportunities for User Interface Architects should continue to increase as the software, web, and mobile industries grow.
Computer Software Engineers
Job Description
Software engineers analyze users’ needs and design, construct, test, and maintain computer applications software or systems. They also solve technical problems that arise. Software engineers can be involved in the design and development of many types of software, including software for operating systems and network distribution, and compilers, which convert programs for execution on a computer. Computer applications software engineers build and maintain general computer applications software or specialized utility programs, while computer systems software engineers coordinate the construction and maintenance of a company’s computer systems and plan their future growth.
Education Requirements
Most employers prefer applicants who have at least a bachelor’s degree in computer science or software engineering. Graduate degrees are preferred for some of the more complex jobs. In 2006, about 80 percent of workers had a bachelor’s degree or higher. Because of increasing emphasis on computer security, software engineers with advanced degrees in mathematics and systems design will be sought after.
Job Outlook
Employment of computer software engineers is projected to increase by 38 percent over the 2006 to 2016 period, which is one of the largest employment increases of any occupation.
Digital Forensics
Job Description
Digital forensics professionals specialize in collecting evidence from computers and digital storage media. They work to recover recover e-mails, images, and data, often from systems that have been compromised or damaged. They analyze systems that have been broken into by hackers. They help conduct investigations and gather evidence, and they can be called on to testify in court. As more crime is conducted and more information and potential evidence is stored digitally, this profession is growing by leaps and bounds.
Education Requirements
Specialized BS degrees are available in computer or digital forensics, and the profession’s unique blend of technical, legal, and law enforcement skills make education a critical part of securing a job.
Job Outlook
Digital forensics is one of the hotter job categories within law enforcement, and it should continue to grow as the country increases funding for homeland security.
Web Developer
Job Description
A Web developer is responsible for the behind-the-scenes code and programming of Web sites and Web-based services. While the edges are often blurred in Web positions, Web developers typically have a more technical orientation than Web designers , who focus on a site’s look and feel, and information architects, who focus on sites’ organization. Web developers’ projects vary widely, ranging from bare-bones active Web pages to complex, multilayered Web applications that might power an ecommerce site.
Education Requirements
Web developers typically have at least a bachelor’s degree, even if they have gained much of their know-how from on-the-job experience. Web developers need to have broad-based knowledge, encompassing areas such as usability and interface design; basic Web skills, such as HTML, CSS and JavaScript; Web 2.0 skills, including Ajax; server-side technologies, such as ASP, PHP and Ruby on Rails; databases such as MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle or IBM’s DB2.
Job Outlook
Computer science and DBA jobs are expected to grow 37 percent from 2006 to 2016. Web developers should continue to enjoy excellent job prospects as the expanding integration of Internet technologies results in a growing need for specialists who can develop and support Internet and intranet applications.
Database Administrators
Job Description
Database administrators work with database management systems software and determine ways to organize and store data. They identify user needs and set up new computer databases. In many cases, database administrators must integrate data from outdated systems into a new system. They also test and coordinate modifications to the system when needed, and troubleshoot problems when they occur. An organization’s database administrator ensures the performance of the system, understands the platform on which the database runs, and adds new users to the system. Because many databases are connected to the Internet, database administrators also must plan and coordinate security measures with network administrators. With the growing volume of sensitive data and the increasing interconnectedness of computer networks, data integrity, backup systems, and database security have become increasingly important aspects of the job of database administrators.
Education Requirements
Most employers seek applicants who have bachelor’s degrees in computer science, information science, or management information systems (MIS).
Job Outlook
Database administrators should continue to enjoy excellent job prospects, with the category expected to grow 29% between 2006 and 2016.
IT Consultant
Job Description
Consulting or contract work has become an increasingly popular form of employment for IT workers. It offers amazing flexibility and comparatively high salaries, though you’ll need to manage your own benefits and spend some time marketing yourself. Employers hire contract workers and consultants from all kinds of IT disciplines, but security, networking, and database professionals are in particularly high demand. Many contract or consulting workers work for staffing agencies. Others strike out on their own and create their own consulting practices.
Education Requirements
Education requirements vary based on which IT discipline you’re consulting in. A BS in Computer Science or Information Technology is a good start, and advanced degrees, such as an MBA are recommended for management positions.
Job Outlook
Consulting and contract work is growing at nearly 10% per year, as more employers move to a hybrid workforce of employees and contractors.
Game Designer
Job Description
Game designers work to create console, PC, and mobile games on a number of different platforms. Many different positions are available in game design, tailored to a variety of skill sets and experience levels. Level Designers work with tools created by the game company to design and populate levels of a game. Systems Designers write code that governs gameplay. Lead or Senior Designers manage team members and often maintain design documents that cover everything from the game’s plot and art direction, to the code used to create it. Game design teams also include more traditional positions, such as Art Directors, Software Engineers, and Release Managers.
Education Requirements
Successful game designers often hold degrees in computer science, 3D Animation, or art, depending on their area of expertise.
Job Outlook
Video gaming is expected to remain one of the fastest growing businesses over the next ten years. As games continue to grow more complex, and production costs continue to rise, positions in game design should grow by leaps and bounds.
Computer Programmers
Job Description
Computer programmers write, test, and maintain software applications. Programmers also conceive, design, and test logical structures for solving problems by computer. Job titles and descriptions may vary, depending on the organization, and this group has a wide range of responsibilities and educational backgrounds. Applications programmers write programs to handle a specific job, such as a program to track inventory within an organization. They also may revise existing packaged software or customize generic applications purchased from vendors. Systems programmers write programs to maintain and control computer systems software, such as operating systems, networked systems, and database systems.
Education Requirements
Almost 8 out of 10 computer programmers held an associate’s degree or higher in 2006; nearly half held a bachelor’s degree, and 2 out of 10 held a graduate degree. Job prospects will be best for applicants with a bachelor’s degree and experience with a variety of programming languages and tools. Obtaining vendor-specific or language-specific certification also can provide a competitive edge.
Job Outlook
Although employment is projected to decline 4%, numerous job openings will result from the need to replace programmers who leave the labor force or transfer to other occupations.
Network Administrators
Job Description
Network administrators, design, test, and evaluate systems such as local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), the Internet, intranets, and other data communications systems. Systems are configured in many ways and can range from a connection between two offices in the same building to globally distributed networks, voice mail, and e-mail systems of a multinational organization. Network systems and data communications analysts perform network modeling, analysis, and planning, often requiring both hardware and software solutions. For example, a network may involve the installation of several pieces of hardware, such as routers and hubs, wireless adapters, and cables, while also requiring the installation and configuration of software, such as network drivers. Analysts also may research related products and make necessary hardware and software recommendations.
Education Requirements
College graduates with a bachelor’s degree in computer science, computer engineering, information science, or MIS also should enjoy favorable prospects, particularly if they have supplemented their formal education with practical experience.
Job Outlook
Network administrators will be in great demand, with the category of network systems and data communications analysts expected to grow 53% between 2006 and 2016.

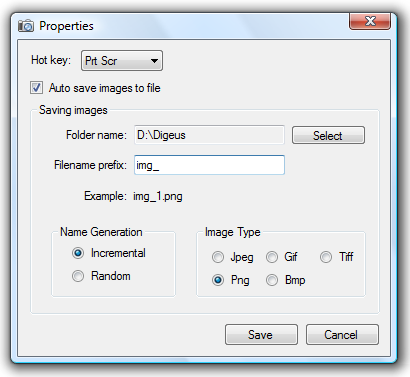

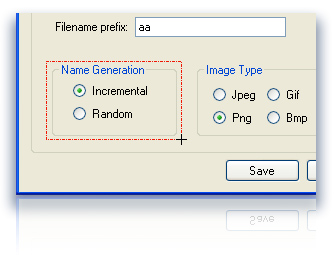
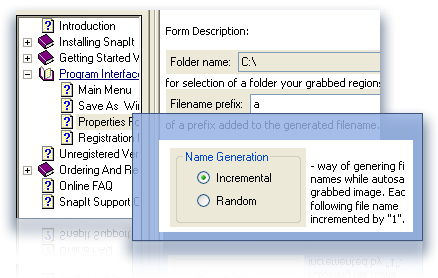
 Supports hotkeys, auto-saving, clipboard
Supports hotkeys, auto-saving, clipboard Automatically copies screenshots to the clipboard
Automatically copies screenshots to the clipboard Tracks capture history, auto-saves captured images
Tracks capture history, auto-saves captured images Saves files in BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG and TIFF formats
Saves files in BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG and TIFF formats Auto-names captured images
Auto-names captured images Crops out sections of vector graphic files such as Fireworks, Adobe Illustrator or Corel without having to flatten the files or open in a new editor
Crops out sections of vector graphic files such as Fireworks, Adobe Illustrator or Corel without having to flatten the files or open in a new editor Irreplaceable tool for Designers, Office Workers, Business People, Analysts and more
Irreplaceable tool for Designers, Office Workers, Business People, Analysts and more Perfect for Technical Writers who have to describe interfaces, menus, buttons, etc.
Perfect for Technical Writers who have to describe interfaces, menus, buttons, etc. Microsoft Windows 95/98/ME/NT/XP/2000/2003/Vista
Microsoft Windows 95/98/ME/NT/XP/2000/2003/Vista Microsoft Framework 2.0
Microsoft Framework 2.0